[알고리즘] 자료구조 - 트리
Table of Contents
트리의 종류 #
- 트리
- 부모-자식의 계층 구조이다.
- 하나의 루트 노드를 갖는다.
- 루트 노드는 0개 이상의 자식을 갖고, 그 자식 또한 0개 이상의 자식을 갖는다.
- 트리는 그래프의 한 종류이다. 사이클(cycle)이 존재할 수 없는 하나의 연결 그래프(connected graph)라고 볼 수 있다.
| 트리 종류 | 의미 |
|---|---|
| 이진트리 (Binary tree) |
자식이 최대 2개인 트리 |
| 완전 이진트리 (Complete binary tree) |
자식이 최대 2개 + 왼쪽부터 꽉꽉 채워짐 |
| 전 이진트리 (Full binary tree) |
자식이 최대 2개 + 자식이 아예 없거나 정확히 2개 있음 |
| 포화 이진트리 (Perfect binary tree) |
전부 자식이 2개 노드의 개수가 정확히 $2^{k-1}$($k$는 트리의 높이) |
| 힙 (Heap) |
자식이 최대 2개 + 왼쪽부터 꽉꽉 채워짐 + 모든 자식 < 부모 (최대힙) or 모든 자식 > 부모 (최소힙) |
| 이진 탐색 트리 (BST; Binary search tree) |
자식이 최대 2개 + 왼쪽 모든 자식 < 부모 < 오른쪽 모든 자식 |
| 균형 트리 (Balenced tree) |
자식이 최대 2개 + 왼쪽 모든 자식 < 부모 < 오른쪽 모든 자식+ 균형 (엄격한 AVL, 약한 레드-블랙 트리) |
힙 #
- (부모노드가 가장 작은 값이 되는, 최소힙을 기준으로 설명하면)
- 삽입
- 밑바닥 가장 오른쪽에 삽입한다.
- 계속 부모와 비교하면서,
해당 노드 < 부모이면 교환하며 올라간다. - $O(\log n)$
- 최소 원소 뽑아내기
- 가장 작은 원소는 루트 노드이므로, 그것을 빼내면 된다. 그 후에는?
- 밑바닥 가장 오른쪽 원소를 루트로 올린다.
- 계속 자식들과 비교하면서,
해당 노드 > 자식이면 교환하며 내려간다. - $O(\log n)$
이진 탐색 트리 #
- 이진 탐색 트리(BST; binary search tree) 는 자식이 최대 2개이면서
왼쪽 모든 자식 < 부모 < 오른쪽 모든 자식과 같은 특징을 가진다. - 검색
- 이진 탐색처럼 절반씩 나눠가며 찾아 내려가기 때문에 트리의 높이인 $O(\log n)$이 걸린다.
- 하지만 균형이 깨져있어서 자식 노드들이 한쪽으로 몰려 있다면 $O(n)$ 이 걸린다.
- 삽입
- 들어갈 위치를 찾는데 트리 높이 만큼의 시간인 $O(\log n)$이 걸린다.
- 위치를 찾았다면 삽입 한다.
- 삭제
- 삭제할 값을 찾은 후
- 자식이 하나이거나 없으면, 삭제할 값을 지우고, 자식을 부모에 연결한다.
- 자식이 둘이면, 오른쪽 자식의 자식들 중에 가장 작은 노드(Successor)를 찾아서 교환하고, 삭제한다.
- 시간 복잡도
- 삭제 대상 노드를 찾는데 그 높이만큼($d$)의 시간이 걸린다.
- 삭제 대상 노드의 서브트리에서 Successor 노드를 찾는다.($h - d$)
- 총 $d + h - d = h = O(\log n)$ 만큼의 시간 복잡도가 걸린다
코드 #
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
Node * left;
Node * right;
};
typedef Node * NodePtr;
class BST
{
private:
NodePtr root;
// 삽입 시간 복잡도? 트리의 높이인 h == log n이 된다.
NodePtr insertNode(NodePtr root, int data)
{
// 트리가 비어 있다면 새로운 노드를 만든다.
if (root == nullptr) return makeNewNode(data);
// 루트보다 작은 값이면 루트의 왼쪽에 추가한다.
// 루트보다 큰 값이면 루트의 오른쪽에 추가한다.
if (root->data > data) root->left = insertNode(root->left, data);
else if (root->data < data) root->right = insertNode(root->right, data);
return root;
}
// 삭제 시간 복잡도?
// 삭제 대상 노드를 찾는데 그 높이만큼(d)의 시간이 걸린다.
// 삭제 대상 노드의 서브트리에서 Successor 노드를 찾는다.(h-d)
// 총 d + h - d 만큼 == h 만큼의 시간 복잡도가 걸린다 == log n
NodePtr deleteNode(NodePtr root, int data)
{
// base case
if (root == nullptr) return root;
// 루트보다 작은 값이면 왼쪽으로 가본다.
// 루트보다 큰 값이면 오른쪽으로 가본다.
if (root->data > data) root->left = deleteNode(root->left, data); // 알아서 삭제된 노드가 부모의 자식으로 연결된다.
else if (root->data < data) root->right = deleteNode(root->right, data);
else // 삭제할 노드를 찾았으면
{
NodePtr temp;
// 자식이 하나거나 없으면, 지우고 자식(data or nullptr)을 부모에 연결한다.
if (root->left == nullptr)
{
temp = root->right;
free(root);
return temp;
}
else if (root->right == nullptr)
{
temp = root->left;
free(root);
return temp;
}
// 자식이 둘이면, 오른쪽 자식 중에 가장 작은 노드를 찾아서 교환하고 삭제한다.
else
{
temp = getSuccessorNode(root->right);
root->data = temp->data;
// 왜 right 일까? 결국 마지막은 root를 리턴하므로. root->right에서 시작했으니. 결과는 root이다.
root->right = deleteNode(root->right, temp->data);
}
}
return root;
}
// 오른쪽 자식 중에 가장 작은 노드를 찾는다.
NodePtr getSuccessorNode(NodePtr root)
{
if (root->left == nullptr) return root;
return getSuccessorNode(root->left);
}
NodePtr search(NodePtr root, int data)
{
if (root == nullptr || root->data == data) return root;
else if (root->data > data) return search(root->left, data);
else if (root->data < data) return search(root->right, data);
return nullptr;
}
void printTree(Node *root, string indent = "", bool last = true)
{
if (root == nullptr) return;
cout << indent;
if (last)
{
cout << "R----";
indent += " ";
}
else
{
cout << "L----";
indent += "| ";
}
cout << root->data << endl;
printTree(root->left, indent, false);
printTree(root->right, indent, true);
}
NodePtr makeNewNode(int data)
{
NodePtr newNode = new Node();
newNode->data = data;
newNode->left = nullptr;
newNode->right = nullptr;
return newNode;
}
public:
BST()
{
root = nullptr;
}
void Insert(int key)
{
root = insertNode(root, key);
}
void Delete(int key)
{
root = deleteNode(root, key);
}
void PrintTree()
{
printTree(root);
}
};
int main()
{
BST* tree = new BST();
tree->Insert(1);
tree->Insert(2);
tree->Insert(3);
tree->Insert(4);
tree->Insert(5);
tree->PrintTree();
tree->Delete(2);
tree->Delete(4);
cout << "After deleting " << endl;
tree->PrintTree();
delete tree;
}
AVL 트리 #
- AVL 트리(Adelson-Velsky and Landis tree)
- 스스로 균형을 잡는 이진 탐색 트리(self-balancing binary search tree)이다.
- 삽입, 검색, 삭제에 늘 $O(\log n)$을 보장한다.
- AVL 트리는 레드-블랙 트리보다 더 엄격하게 균형이 잡혀 있기 때문에, 삽입과 삭제를 할 때 최악의 경우에는 더 많은 회전(rotations)이 필요하다.
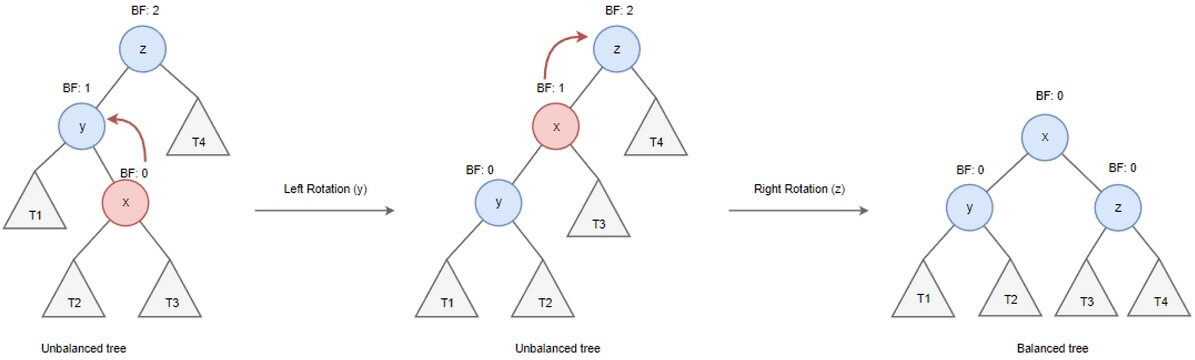
- Balance Factor
왼쪽 서브트리의 높이 - 오른쪽 서브트리의 높이인 BF를 기준으로 높이 차이를 구해서 균형을 판단한다.- AVL트리는 BF가 $1$에서 $-1$ 사이가 되는 균형 상태를 유지한다.
- 만약 BF가 $2$ 혹은 $-2$인 불균형이 되면 회전(rotation) 을 통해 균형을 잡는다.
- 불균형은 LR, LL, RL, RR 의 총 4 가지의 형태로 존재한다.
- $2$ 만큼 불균형이라면, 왼쪽 서브트리가 오른쪽 서브트리보다 더 높은 것이다.
- 이때, 오른쪽으로 추가된 노드가 있는 경우 LR (Left Right) 형태라고 한다.
- 이때, 왼쪽으로 추가된 노드가 있는 경우 LL (Left Left) 형태라고 한다.
- LR 불균형일 경우,
LR → 왼쪽 회전 → LL → 오른쪽 회전 → 균형으로 균형을 맞추고, - LL 불균형일 경우,
LL → 오른쪽 회전 → 균형으로 균형을 맞추면 된다.
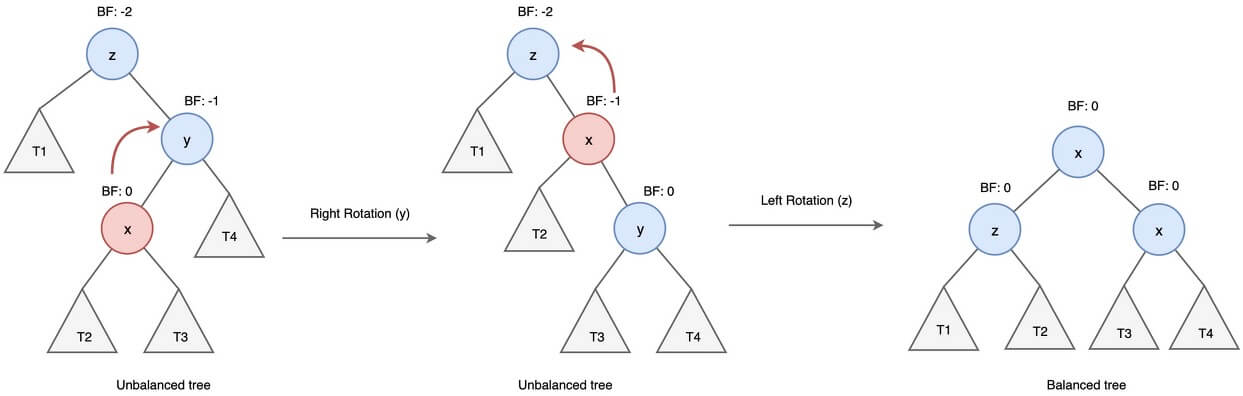
- $-2$ 만큼 불균형이라면, 오른쪽 서브트리가 왼쪽 서브트리보다 더 높은 것이다.
- 이때, 왼쪽으로 추가된 노드가 있는 경우 RL (Right Left) 형태라고 한다.
- 이때, 오른쪽으로 추가된 노드가 있는 경우 RR (Right Right) 형태라고 한다.
- RL 불균형일 경우,
RL → 오른쪽 회전 → RR → 왼쪽 회전 → 균형으로 균형을 맞추고, - RR 불균형일 경우,
RR → 왼쪽 회전 → 균형으로 균형을 맞추면 된다.
코드 #
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
Node * left;
Node * right;
int height;
};
typedef Node * NodePtr;
class AVLTree
{
private:
NodePtr root;
NodePtr insertNode(NodePtr node, int key)
{
// 새노드와 루트를 비교해서
// 새노드가 작으면 : 왼쪽에 삽입
// 새노드가 크면 : 오른쪽에 삽입
if (node == nullptr) return (newNode(key));
if (key < node->data) node->left = insertNode(node->left, key);
else if (key > node->data) node->right = insertNode(node->right, key);
else return node;
// 새로워진 노드의 높이 계산
node->height = 1 + max(height(node->left), height(node->right));
// Balance Factor에 따라 균형 맞추기
int balanceFactor = getBalanceFactor(node);
// 왼쪽 서브 트리가 높다.
if (balanceFactor > 1)
{
// 루트의 왼쪽 자식의 왼쪽에 노드가 추가되었다.
if (key < node->left->data)
{
return rightRotate(node);
}
// 루트의 왼쪽 자식의 오른쪽에 노드가 추가되었다.
else if (key > node->left->data)
{
node->left = leftRotate(node->left);
return rightRotate(node);
}
}
// 오른쪽 서브 트리가 높다.
else if (balanceFactor < -1)
{
// 루트의 오른쪽 자식의 오른쪽에 노드가 추가되었다.
if (key > node->right->data)
{
return leftRotate(node);
}
// 루트의 오른쪽 자식의 왼쪽에 노드가 추가되었다.
else if (key < node->right->data)
{
node->right = rightRotate(node->right);
return leftRotate(node);
}
}
return node;
}
NodePtr deleteNode(NodePtr root, int key)
{
// 위치를 찾아서 삭제한다.
if (root == nullptr) return root;
if (key < root->data) root->left = deleteNode(root->left, key);
else if (key > root->data) root->right = deleteNode(root->right, key);
// root == 삭제할 노드
else
{
if ((root->left == nullptr) || (root->right == nullptr))
{
NodePtr temp = root->left ? root->left : root->right;
// 자식이 없으면 temp == root 삭제
if (temp == nullptr)
{
temp = root;
root = nullptr;
}
// 한쪽 자식이 있으면 자식을 root 자리로 올리고 삭제
else
{
*root = *temp;
}
free(temp);
}
// 자식이 둘 다 있으면
else
{
// 오른쪽 서브트리에서 가장 작은 노드(successor)를 찾는다.
NodePtr temp = getSuccessorNode(root->right);
// 삭제하려는 노드(root)에 successor의 값을 대입해서 옮긴다.
root->data = temp->data;
// 대입한 후 남겨진 successor 노드를 오른쪽 서브트리에서 삭제한다.
root->right = deleteNode(root->right, temp->data);
}
}
if (root == nullptr) return root;
// 새로워진 노드의 높이 계산
root->height = 1 + max(height(root->left), height(root->right));
// Balance Factor에 따라 균형 맞추기
int balanceFactor = getBalanceFactor(root);
// 왼쪽 서브 트리가 높다.
if (balanceFactor > 1)
{
// 루트의 왼쪽 자식의 왼쪽에 노드가 많다.
if (getBalanceFactor(root->left) >= 0)
{
return rightRotate(root);
}
// 루트의 왼쪽 자식의 오른쪽에 노드가 많다.
else
{
root->left = leftRotate(root->left);
return rightRotate(root);
}
}
// 오른쪽 서브 트리가 높다.
else if (balanceFactor < -1)
{
// 루트의 오른쪽 자식의 오른쪽에 노드가 많다.
if (getBalanceFactor(root->right) <= 0)
{
return leftRotate(root);
}
// 루트의 오른쪽 자식의 왼쪽에 노드가 많다.
else
{
root->right = rightRotate(root->right);
return leftRotate(root);
}
}
return root;
}
NodePtr rightRotate(NodePtr x)
{
// z z
// x -> y
// y x
// x y
// y -> z x
// z
NodePtr y = x->left;
// [y의 오른쪽 자식 처리]
// y의 오른쪽 자식은 x의 왼쪽 자식이 된다.
x->left = y->right;
// x의 왼쪽 자식이었던 y가
// x를 오른쪽 자식으로 삼는 부모가 된다.
y->right = x;
// 높이 갱신
x->height = max(height(x->left), height(x->right)) + 1;
y->height = max(height(y->left), height(y->right)) + 1;
// 새로운 루트노트 y
return y;
}
NodePtr leftRotate(NodePtr x)
{
// z z
// x -> y
// y x
// x y
// y -> x z
// z
NodePtr y = x->right;
// [y의 왼쪽 자식 처리]
// y의 왼쪽 자식은 x의 오른쪽 자식이 된다.
x->right = y->left;
// x의 오른쪽 자식이었던 y가
// x를 왼쪽 자식으로 삼는 부모가 된다.
y->left = x;
// 높이 갱신
x->height = 1 + max(x->left->height, x->right->height);
y->height = 1 + max(y->left->height, y->right->height);
// 새로운 루트노트 y
return y;
}
int max(int a, int b)
{
return (a > b) ? a : b;
}
int height(NodePtr node)
{
if (node == nullptr) return 0;
return node->height;
}
int getBalanceFactor(NodePtr node)
{
if (node == nullptr) return 0;
return height(node->left) - height(node->right);
}
// 가장 작은 노드를 찾는다.
NodePtr getSuccessorNode(NodePtr root)
{
if (root->left == nullptr) return root;
return getSuccessorNode(root->left);
}
void printTree(NodePtr root, string indent = "", bool last = true)
{
if (root == nullptr) return;
cout << indent;
if (last)
{
cout << "R----";
indent += " ";
}
else
{
cout << "L----";
indent += "| ";
}
cout << root->data << endl;
printTree(root->left, indent, false);
printTree(root->right, indent, true);
}
NodePtr newNode(int data)
{
NodePtr node = new Node();
node->data = data;
node->left = nullptr;
node->right = nullptr;
node->height = 1;
return node;
}
public:
AVLTree()
{
root = nullptr;
}
void Insert(int key)
{
root = insertNode(root, key);
}
void Delete(int key)
{
deleteNode(root, key);
}
void PrintTree()
{
printTree(root);
}
};
int main()
{
AVLTree * tree = new AVLTree();
tree->Insert(33);
tree->Insert(13);
tree->Insert(53);
tree->Insert(9);
tree->Insert(21);
tree->Insert(61);
tree->Insert(8);
tree->Insert(11);
tree->PrintTree();
tree->Delete(13);
cout << "After deleting " << endl;
tree->PrintTree();
delete tree;
}
레드-블랙 트리 #
- 레드-블랙 트리(Red-black tree)
- 스스로 균형을 잡는 이진 탐색 트리(self-balancing binary search tree)이다.
- 삽입, 검색, 삭제에 늘 $O(\log n)$을 보장한다.
- 레드-블랙 트리는 이진 탐색 트리의 특성에다 다음과 같은 조건이 추가된다.
| 순서 | 명칭 | 설명 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Root Property |
루트 노드는 Black이다. |
| 2 | External Property |
모든 단말 노드들은 Black이다. |
| 3 | Internal Property |
Red 노드의 자식 양쪽은 언제나 Black이다. - No Double Red (Red 노드가 연속으로 나올 수 없다.) |
| 4 | Depth Property |
어떤 노드에서 하위 단말 노드들에 도달하는 모든 경로의 Black 노드 개수는 같다. |
- 이런 조건들에 의해서 다음과 같이 균형이 잡힌다.
- 3번 조건에 따르면 Red 노드가 연속으로 나올 수 없다. 그래서 최단 경로는 모두 Black 노드로만 구성되어 있다고 했을 때, 최장 경로는 Black 노드와 Red 노드가 번갈아 나오는 것이 될 것이다.
- 여기에 4번 조건에 따라서 모든 경로에서 Black 노드의 수가 같다고 했기 때문에, 존재하는 모든 경로에 대해 최장 경로의 거리는 최단 경로의 거리의 두 배 이상이 될 수 없다.
- 다시 말해서 레드-블랙 트리는 개략적(roughly)으로 균형이 잡혀 있다(balanced). 따라서, 삽입, 삭제, 검색시 최악의 경우에서의 시간복잡도가 트리의 높이에 따라 결정되기 때문에 보통의 이진 탐색 트리에 비해 효율적이라고 할 수 있다.
삽입 #
- 설명에 앞서, 노드의 이름을 이렇게 정한다.
N는 삽입된 현재 노드P는 삽입된 노드의 부모 노드G는 삽입된 노드의 조부모 노드U는 삽입된 노드의 삼촌 노드(G의 자식이며P의 형제이다)
- 조건에 위반이 될 수 있는 경우는 두 가지를 생각해볼 수 있다.
- Red 위반
- Red 노드가 Red 자식 노드를 가지고 있다.
- Black 위반
- 어떤 경로에 Black 노드가 더 많다.
- Red 위반
- 삽입 노드는 Red이므로 Black 위반은 발생할 수 없다. 따라서 Red 위반을 고려해본다.
- Red 위반이기 때문에
N,P는 모두 Red이겠다. - 그리고 그 전에는 위반이 없었으므로
G는 Black이겠다. - 우리가 알 수 없는 것은 다음과 같다.
U는 무슨 색인지 모른다.N,P가 어느쪽 자식인지 모른다.
- 모르는 것들을 가지고 각각의 case를 고려해서 트리의 균형을 유지해보자.
- Red 위반이기 때문에
- Red 위반 시(
N,P가 모두 Red일 때) case들
| 번호 | 조건 | 해결법 |
|---|---|---|
| case 1 | U가 Red |
P, U, G의 색깔을 변경한다.(Recolor) 그리고 재귀적으로 루트까지 적용해나간다. |
| case 2 | U가 Black |
|
| case 2.1 | P가 오른쪽자식 N이 왼쪽자식 |
P를 기준으로 오른쪽 회전을 하고, G를 기준으로 왼쪽 회전을 한다. Recolor |
| case 2.2 | P가 오른쪽자식 N이 오른쪽자식 |
G를 기준으로 왼쪽 회전을 한다. Recolor |
| case 2.3 | P가 왼쪽자식 N이 오른쪽자식 |
P를 기준으로 왼쪽 회전을 하고, G를 기준으로 오른쪽 회전을 한다. Recolor |
| case 2.4 | P가 왼쪽자식 N이 왼쪽자식 |
G를 기준으로 오른쪽 회전을 한다. Recolor |
삭제 #
- 설명에 앞서, 노드의 이름을 이렇게 정한다.
X는 삭제할 노드P는 삭제할 노드의 부모 노드S는 삭제할 노드의 형제
- 이진 탐색 트리의 규칙에 따라서 노드를 삭제한다.
- 삭제하려는 노드의 자식이 양쪽 다 있을 경우에는 오른쪽 서브 트리에서의 최솟값인 Successor 노드를 찾아 교환한다.
- 이 때, Successor 노드는 가장 작은 값이기 때문에(끝부분) 자식이 없거나 혹은 오른쪽에 하나만 있음을 알 수 있다.
- 삭제하려는 노드가 Red라면, Red를 삭제하는 것은 문제가 안 되므로 (Black의 개수가 중요했다) 그냥 삭제한다.
- 하지만 Black이라면 살펴봐야하겠다.
| 번호 | 조건 | 해결법 |
|---|---|---|
| case 1 | X가 Red |
그냥 삭제한다 |
| case 2 | X가 Black |
|
| case 2.1 | S가 Red |
S와 P의 색깔을 변경한다. P를 기준으로 왼쪽으로 회전한다. 그리고 바뀐 위치의 S부터 다시 본다. |
| case 2.2 | S의 양쪽 자식이 Black |
S의 색깔을 변경한다. |
| case 2.3 | S의 오른쪽 자식이 Black |
S와 그의 왼쪽 자식의 색깔을 변경한다. S를 기준으로 오른쪽으로 회전한다. 그리고 아래의 과정을 거친다. |
| case 2.4 | S의 오른쪽 자식이 Red |
P, S와 그의 오른쪽 자식의 색깔을 변경한다. P를 기준으로 왼쪽으로 회전한다. |
코드 #
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
enum Color { Black, Red };
struct Node
{
int data;
Node * parent;
Node * left;
Node * right;
Color color;
};
typedef Node * NodePtr;
class RBTree
{
private:
NodePtr root;
NodePtr TNULL; // 단말 노드
void insertNodeHelper(int key)
{
NodePtr node = newNode(key);
NodePtr y = nullptr;
NodePtr x = this->root;
// 이진 탐색 트리 규칙에 따라서 맞는 위치에 있는
// 리프 노드 x를 찾는다.
// y는 x의 부모이다.
while (x != TNULL)
{
y = x;
if (node->data < x->data) x = x->left;
else x = x->right;
}
// 새로운 노드의 부모를 y로 만든다.
node->parent = y;
if (y == nullptr) root = node;
else if (node->data < y->data) y->left = node;
else y->right = node;
// 새로운 노드가 루트 노드이면 검은색으로 만들고 리턴한다.
if (node->parent == nullptr)
{
node->color = Black;
return;
}
// 새로운 노드의 부모가 루트 노드이면 리턴한다.
if (node->parent->parent == nullptr)
return;
// 조부모까지 존재한다면 (깊이 3) 규칙에 맞게 트리를 손본다.
fixInsert(node);
}
void fixInsert(NodePtr node)
{
// G
// P U
// N
NodePtr u;
// 삽입 시 발생하는 빨간색 위반(N과 P가 모두 빨간색)인 경우 수정이 필요하다.
while (node->parent->color == Red)
{
if (node->parent == node->parent->parent->right)
{
u = node->parent->parent->left;
// case 1
// U가 빨간색인 경우에는
// P, U, G의 색깔을 변경한다.
if (u->color == Red)
{
node->parent->color = Black; // P : Black
u->color = Black; // U : Black
node->parent->parent->color = Red; // G : Red
// G를 node로 보고 거기부터 다시 본다.
node = node->parent->parent;
}
// U가 검은색이고 P가 오른쪽 자식인 경우에는
else
{
// case 2.1
// N이 왼쪽 자식이라면
// P를 기준으로 오른쪽 회전을 하고,
// G를 기준으로 왼쪽 회전을 한다.
// G G N
// U P -> U N -> G P
// N P U
if (node == node->parent->left)
{
node = node->parent;
rightRotate(node);
}
// case 2.2
// N이 오른쪽 자식이라면
// G를 기준으로 왼쪽 회전을 한다.
// G P
// U P -> G N
// N U
// 노드의 부모와 조부모 색상을 바꾼다.
// red(P)
// black(G) red
// black
node->parent->color = Black; // 부모 : Black
node->parent->parent->color = Red; // 조부모 : Red
leftRotate(node->parent->parent);
}
}
else
{
u = node->parent->parent->right;
// case 1
// U가 빨간색인 경우에는
// P, U, G의 색깔을 변경한다.
if (u->color == Red)
{
node->parent->color = Black; // P : Black
u->color = Black; // U : Black
node->parent->parent->color = Red; // G : Red
// G를 N으로 만들고 거기부터 다시 본다.
node = node->parent->parent;
}
// U가 검은색이고 P가 왼쪽 자식인 경우에는
else
{
// case 2.3
// N이 오른쪽 자식이라면
// P를 기준으로 왼쪽 회전을 하고,
// G를 기준으로 오른쪽 회전을 한다.
// G G N
// P U -> N U -> P G
// N P U
if (node == node->parent->right)
{
node = node->parent;
leftRotate(node);
}
// case 2.4
// N이 왼쪽 자식이라면
// G를 기준으로 오른쪽 회전을 한다.
// G P
// P U -> N G
// N U
// 노드의 부모와 조부모 색상을 바꾼다.
// red(P)
// red black(G)
// black
node->parent->color = Black; // 부모 : Black
node->parent->parent->color = Red; // 조부모 : Red
rightRotate(node->parent->parent);
}
}
if (node == root) break;
}
root->color = Black;
}
void deleteNodeHelper(NodePtr node, int key)
{
NodePtr z = TNULL;
NodePtr x, y;
// 이진 탐색 트리 규칙에 따라서 node를 옮기면서 key를 가진 노드를 찾는다.
// 결과적으로 삭제하려는 노드가 z가 된다.
while (node != TNULL)
{
if (node->data == key)
z = node;
if (node->data <= key) node = node->right;
else node = node->left;
}
// 찾은 z가 리프 노드라면 그런 키를 가진 노드가 없는 것이다.
if (z == TNULL)
{
cout << "Couldn't find key in the tree" << endl;
return;
}
y = z;
int y_original_color = y->color;
// 이진 탐색 트리의 규칙에 따라
// 삭제하려는 노드의
// 왼쪽이 빈 노드라면, 오른쪽 노드를 삭제할 위치로 옮긴다.
if (z->left == TNULL)
{
// x는 결과적으로, 삭제하는 노드의 오른쪽 자식 위치이다.
// 그리고 삭제하는 노드와 뒤바꾼 자리이다.
x = z->right;
rbTransplant(z, z->right);
}
// 오른쪽이 빈 노드라면, 왼쪽 노드를 삭제할 위치로 옮긴다.
else if (z->right == TNULL)
{
x = z->left;
rbTransplant(z, z->left);
}
// 양쪽 다 자식이 있다면
else
{
// successor 노드를 찾는다.
y = getMinimumNode(z->right);
y_original_color = y->color;
// x는 결과적으로 successor 노드의 오른쪽 자식 위치이다.
// 그리고 삭제하려는 노드 <- sucessor 노드 <- x 처럼 이동한 자리이다.
x = y->right;
if (y->parent == z)
{
x->parent = y;
}
else
{
// successor 노드의 오른쪽 자식을 successor 노드 자리에 놓는다.
rbTransplant(y, y->right);
// 삭제하려는 노드의 오른쪽을 successor 노드의 오른쪽으로 만든다.
y->right = z->right;
y->right->parent = y;
}
// 삭제하려는 노드 자리에 successor 노드를 놓는다.
rbTransplant(z, y);
y->left = z->left;
y->left->parent = y;
y->color = z->color;
}
delete z;
// 만약에 삭제한 노드의 색상이 Black이라면
// 자리를 바꾼 위치인 x부터 트리를 손본다.
if (y_original_color == Black)
fixDelete(x);
}
void fixDelete(NodePtr x)
{
NodePtr s;
while (x != root && x->color == Black)
{
if (x == x->parent->left)
{
s = x->parent->right;
// N이 Black인데 S가 Red이면
// P를 기준으로 왼쪽으로 회전한다.
if (s->color == Red)
{
// P S
// N S -> P .
// . . N .
// case 2.1
s->color = Black; // S : Black
x->parent->color = Red; // P : Red
leftRotate(x->parent);
// 바뀐 N의 위치에 따라 형제의 위치도 맞게 설정한다.
s = x->parent->right;
}
// S의 양쪽 자식이 모두 Black이면
// S의 색깔을 Red로 바꾼다.
// case 2.2
if (s->left->color == Black && s->right->color == Black)
{
s->color = Red; // S : Red
// 한 칸 위로 올라가며 계속 본다.
x = x->parent;
}
else
{
// S의 오른쪽 자식이 Black이면
// case 2.3
if (s->right->color == Black)
{
s->left->color = Black; // S의 왼쪽자식 : Black
s->color = Red; // S : Red
rightRotate(s);
s = x->parent->right;
}
// S의 오른쪽 자식이 Red이면
// case 2.4
s->color = x->parent->color; // S : P
x->parent->color = Black; // P : Black
s->right->color = Black; // S의 오른쪽 자식 : Black
leftRotate(x->parent);
x = root;
}
}
else
{
s = x->parent->left;
if (s->color == Red)
{
// case 2.1
s->color = Black;
x->parent->color = Red;
rightRotate(x->parent);
s = x->parent->left;
}
if (s->right->color == Black && s->right->color == Black)
{
// case 2.2
s->color = Red;
x = x->parent;
}
else
{
if (s->left->color == Black)
{
// case 2.3
s->right->color = Black;
s->color = Red;
leftRotate(s);
s = x->parent->left;
}
// case 2.4
s->color = x->parent->color;
x->parent->color = Black;
s->left->color = Black;
rightRotate(x->parent);
x = root;
}
}
}
x->color = Black;
}
void rbTransplant(NodePtr deleteThis, NodePtr moveThis)
{
// deleteThis의 자리에 moveThis를 옮긴다.
if (deleteThis->parent == nullptr) root = moveThis;
else if (deleteThis == deleteThis->parent->left) deleteThis->parent->left = moveThis;
else deleteThis->parent->right = moveThis;
moveThis->parent = deleteThis->parent;
}
// 왼쪽 회전
void leftRotate(NodePtr x)
{
// z z
// x -> y
// y x
// x y
// y -> x z
// z
// x의 오른쪽 자식이었던 y가
// x를 왼쪽 자식으로 삼는 부모가 된다.
NodePtr y = x->right;
// [y의 왼쪽 자식 처리]
// y의 왼쪽 자식은 x의 오른쪽 자식이 된다.
x->right = y->left;
if (y->left != TNULL)
y->left->parent = x;
// [y의 부모 처리]
// x가 루트였다면 y를 루트로
// x가 왼쪽 자식이었으면 y를 왼쪽 자식으로
// x가 오른쪽 자식이었으면 y를 오른쪽 자식으로
y->parent = x->parent;
if (x->parent == nullptr) this->root = y;
else if (x == x->parent->left) x->parent->left = y;
else x->parent->right = y;
// [x, y 연결]
y->left = x;
x->parent = y;
}
// 오른쪽 회전
void rightRotate(NodePtr x)
{
// z z
// x -> y
// y x
// x y
// y -> x z
// z
// x의 왼쪽 자식이었던 y가
// x를 오른쪽 자식으로 삼는 부모가 된다.
NodePtr y = x->left;
// [y의 오른쪽 자식 처리]
// y의 오른쪽 자식은 x의 왼쪽 자식이 된다.
x->left = y->right;
if (y->right != TNULL)
y->right->parent = x;
// [y의 부모 처리]
// x가 루트였다면 y를 루트로
// x가 왼쪽 자식이었으면 y를 왼쪽 자식으로
// x가 오른쪽 자식이었으면 y를 오른쪽 자식으로
y->parent = x->parent;
if (x->parent == nullptr) this->root = y;
else if (x == x->parent->right) x->parent->right = y;
else x->parent->left = y;
// [x, y 연결]
y->right = x;
x->parent = y;
}
NodePtr getMinimumNode(NodePtr node)
{
while (node->left != TNULL)
node = node->left;
return node;
}
NodePtr getMaximumNode(NodePtr node)
{
while (node->right != TNULL)
node = node->right;
return node;
}
NodePtr getSuccessorNode(NodePtr node)
{
// 오른쪽 서브트리에서 제일 작은 노드이다.
if (node->right != TNULL)
return getMinimumNode(node->right);
// 만약에 오른쪽 노드가 없다면,
// 해당 노드가 오른쪽 자식인 부모로 계속 올라간다.
NodePtr res = node->parent;
while (res != TNULL && node == res->right)
{
node = res;
res = res->parent;
}
return res;
}
NodePtr getPredecessorNode(NodePtr node)
{
// 왼쪽 서브트리에서 제일 큰 노드이다.
if (node->left != TNULL)
return getMaximumNode(node->left);
// 만약에 왼쪽 노드가 없다면,
// 해당 노드가 왼쪽쪽 자식인 부모로 계속 올라간다.
NodePtr res = node->parent;
while (res != TNULL && node == res->left)
{
node = res;
res = res->parent;
}
return res;
}
NodePtr searchTreeHelper(NodePtr node, int key)
{
if (node == TNULL || key == node->data)
return node;
if (key < node->data)
return searchTreeHelper(node->left, key);
return searchTreeHelper(node->right, key);
}
void preOrderHelper(NodePtr node)
{
if (node == TNULL) return;
cout << node->data << " ";
preOrderHelper(node->left);
preOrderHelper(node->right);
}
void inOrderHelper(NodePtr node)
{
if (node == TNULL) return;
inOrderHelper(node->left);
cout << node->data << " ";
inOrderHelper(node->right);
}
void postOrderHelper(NodePtr node)
{
if (node == TNULL) return;
postOrderHelper(node->left);
postOrderHelper(node->right);
cout << node->data << " ";
}
void printHelper(NodePtr root, string indent, bool last)
{
if (root == TNULL) return;
cout << indent;
if (last)
{
cout << "R----";
indent += " ";
}
else
{
cout << "L----";
indent += "| ";
}
string curColor = root->color ? "RED" : "BLACK";
cout << root->data << "(" << curColor << ")" << endl;
printHelper(root->left, indent, false);
printHelper(root->right, indent, true);
}
NodePtr getRoot()
{
return this->root;
}
void initializeNULLNode(NodePtr node, NodePtr parent)
{
node->data = 0;
node->parent = parent;
node->left = nullptr;
node->right = nullptr;
node->color = Black;
}
Node * newNode(int key)
{
NodePtr node = new Node;
node->parent = nullptr;
node->data = key;
node->left = TNULL;
node->right = TNULL;
node->color = Red; // 새 노드는 늘 Red이다.
return node;
}
public:
RBTree()
{
TNULL = new Node;
initializeNULLNode(TNULL, nullptr);
root = TNULL;
}
void InsertNode(int key)
{
insertNodeHelper(key);
}
void DeleteNode(int key)
{
deleteNodeHelper(this->root, key);
}
NodePtr SearchNode(int key)
{
return searchTreeHelper(this->root, key);
}
void PrintPreorder()
{
preOrderHelper(this->root);
}
void PrintInorder()
{
inOrderHelper(this->root);
}
void PrintPostorder()
{
postOrderHelper(this->root);
}
void PrintTree()
{
if (root) printHelper(this->root, "", true);
}
};
int main()
{
RBTree * tree = new RBTree();
tree->InsertNode(8);
tree->InsertNode(18);
tree->InsertNode(5);
tree->InsertNode(15);
tree->InsertNode(17);
tree->InsertNode(25);
tree->InsertNode(40);
tree->InsertNode(80);
tree->DeleteNode(25);
tree->PrintTree();
delete tree;
}
트리의 순회 #
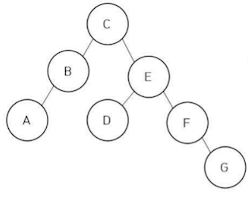
| 트리 순회 방식 | 순서 | 예제 결과 |
|---|---|---|
| 전위 순회 (Preorder) | 방문 Left Right | C B A E D F G |
| 중위 순회 (Inorder) | Left 방문 Right | A B C D E F G |
| 후위 순회 (Postorder) | Left Right 방문 | A B D G F E C |
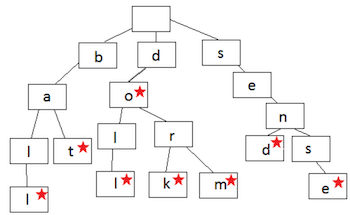
트라이 #
- 트라이(trie) = 접두사 트리(prefix tree)
- $K$-진 트리 구조를 통해 문자열을 저장하는 방식이다. ($K$는 단어 개수)
- 접두사를 빠르게 찾아볼 수 있다.
- 길이가 $K$인 문자열은 $O(K)$만에 유효한 접두사인지 확인할 수 있다.
- 자동완성 기능, 사전 검색 등 문자열을 탐색하는데 특화되어있는 자료구조다.
- 각 노드에 문자를 저장하고, 트리를 아래쪽으로 순회하면 단어 하나가 나온다.
- 단어의 끝은 널 노드(null node)인
*노드로 나타내거나 플래그로 나타낼 수 있다. - 각 노드는 [ 널 노드를 사용한다면 1개(플래그라면 0개) ~ 알파벳 개수 + 1개 ]까지 자식을 갖고 있을 수 있다.
References #
- 코딩 인터뷰 완전 분석
- https://algorithmtutor.com/Data-Structures/Tree/Red-Black-Trees/
- https://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/레드-블랙_트리